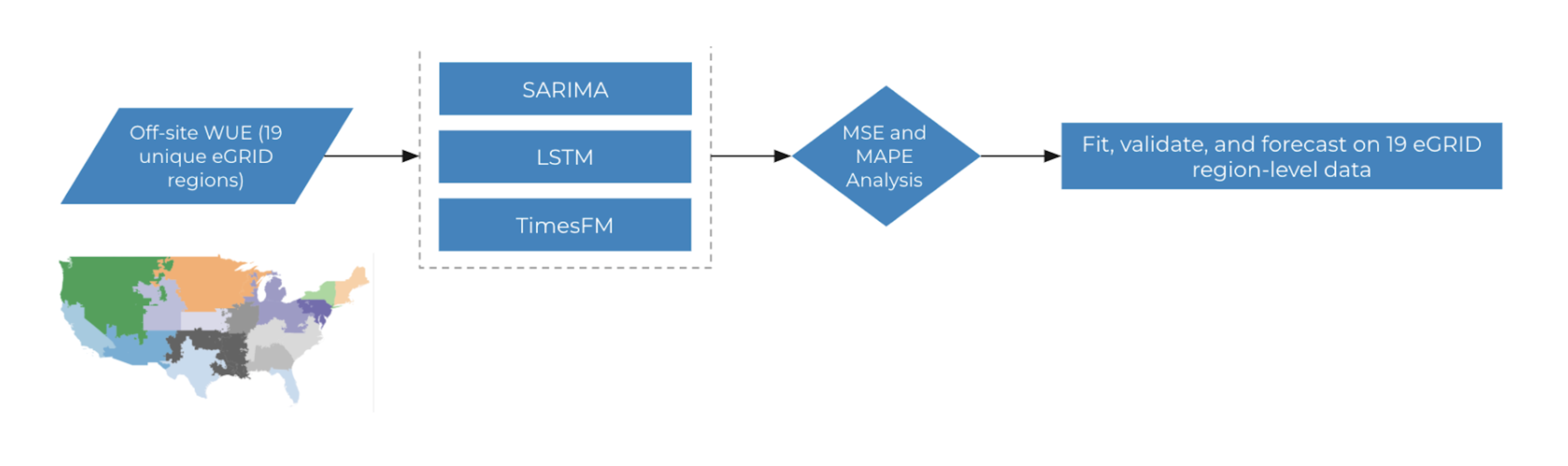
Off-site WUE
Our off-site models provide needed information for data center operators looking to decrease their water footprint by minimizing off-site water usage via energy generation, which accounts for ~75% of their water usage. We trained 19 models for each represented eGRID region in our off-site dataset. Every city that falls in the same eGRID region has the same off-site WUE prediction forecast, as they share similar embedded power source mixes (proportions of energy coming from sources like natural gas, nuclear, hydro, etc. that vary in terms of their embedded water usage). We are equipped with hourly data for 19 geographically partitioned EGRID regions across the United States, where all cities in the same region share the same off-site water usage efficiency (WUE), which comes from indirect usage of water via electricity generation. This reduces our problem space compared to the distributed and localized on-site WUE forecasts, which thereby allows us to compare and contrast more complex modelling methodologies (e.g LSTM, SARIMA, and TimesFM — Google's new foundation model for forecasting). After exploring an LSTM and a pre-trained model called TimesFM, we decided to use a classical forecast modeling method called SARIMA (seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average for our off-site data to predict future WUE because of its comparable performance to the other models as measured by RMSE, MAE, and MAPE metrics. This model takes advantage of seasonal patterns, which can improve the fit to training data and enhance prediction capability. Our process for creating these 72hrs ahead forecasts is demonstrated in the following diagram: